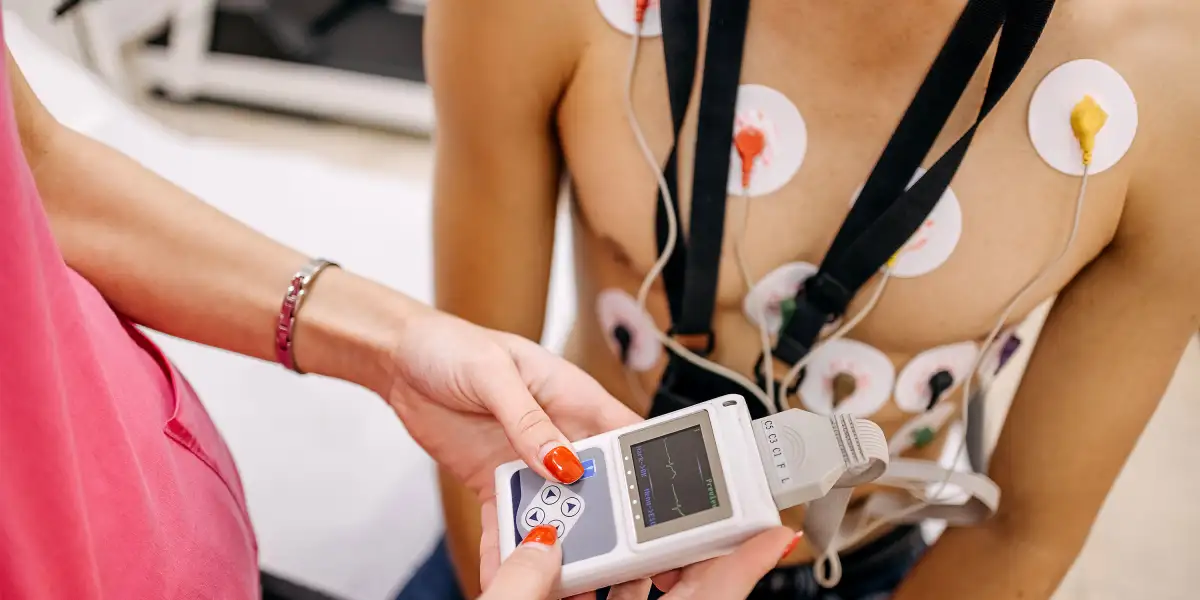
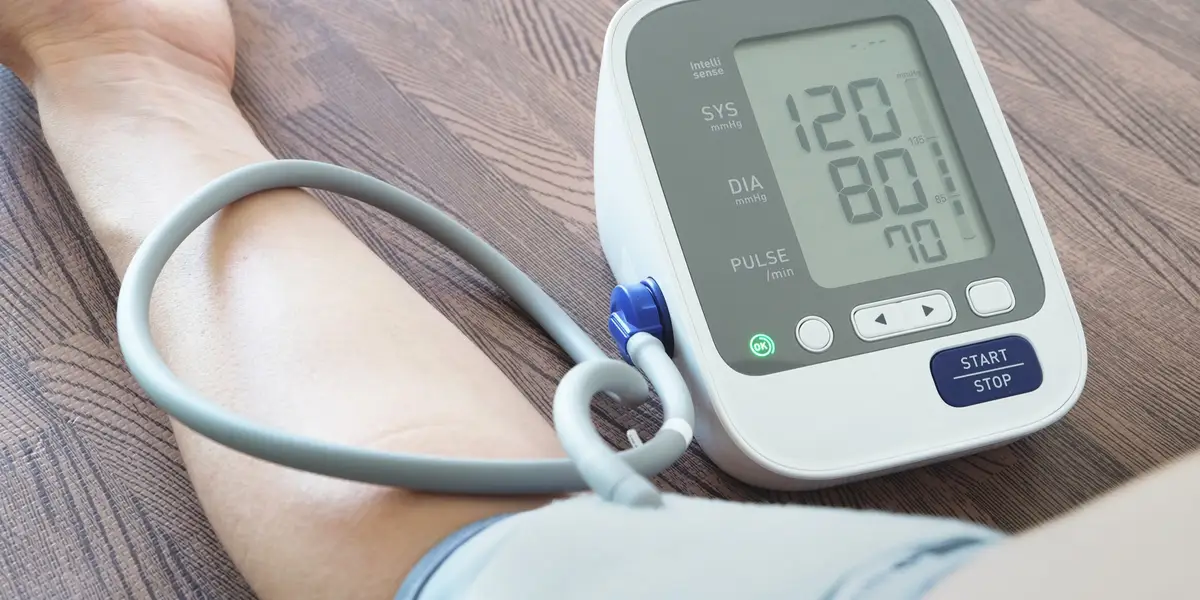
Irregular heartbeat, or arrhythmia, is a condition where the heart beats too fast, too slow, or irregularly. It can lead to serious complications, including stroke, heart failure, and even sudden cardiac arrest. Detecting irregular heartbeats early is crucial for timely intervention and effective management. In recent years, advancements in technology have revolutionized the detection and monitoring of irregular heartbeats, offering innovative solutions that enhance both accuracy and accessibility.
Before delving into detection methods, it’s essential to grasp the intricacies of irregular heartbeat. The heart’s rhythm is controlled by electrical signals that coordinate its contractions. When these signals become disrupted, arrhythmias occur. Common types include atrial fibrillation (AFib), bradycardia (slow heartbeat), and tachycardia (fast heartbeat). Symptoms can vary from palpitations and dizziness to chest pain and fainting spells.
Traditional Detection Methods:
Historically, irregular heartbeat detection relied on clinical examination, electrocardiograms (ECGs), and Holter monitors. While effective, these methods often require specialized equipment and trained professionals, limiting their accessibility and efficiency. Additionally, they offer only intermittent snapshots of heart activity, potentially missing transient arrhythmias.
Innovative Technologies:
- Wearable Devices: The advent of wearable technology has democratized heart monitoring. Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and portable ECG monitors now offer continuous heart rate monitoring, alerting users to irregularities in real-time. Companies like Apple and Fitbit have integrated ECG capabilities into their devices, empowering users to proactively manage their heart health.
- Mobile Applications: Mobile apps equipped with heart rate monitoring algorithms have emerged as valuable tools for irregular heartbeat detection. These apps utilize smartphone cameras or external sensors to measure heart rate variability and identify arrhythmias. Some even incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) for enhanced accuracy and personalized insights.
- Implantable Devices: For individuals with recurrent or severe arrhythmias, implantable devices provide long-term monitoring and intervention. Implantable loop recorders (ILRs) and pacemakers equipped with arrhythmia detection algorithms continuously monitor heart activity, transmitting data to healthcare providers for analysis. These devices offer unparalleled insights into cardiac function, enabling timely intervention and treatment adjustments.
- Machine Learning and AI: The integration of machine learning and AI algorithms has revolutionized arrhythmia detection. These algorithms analyze vast amounts of physiological data, identifying patterns indicative of irregular heartbeats with high accuracy. By continuously learning from new data, AI-powered systems adapt and improve over time, enhancing diagnostic precision and predictive capabilities.
Importance of Early Detection:
Early detection of irregular heartbeat is paramount for several reasons:
- Prevention of Complications: Timely identification allows for prompt intervention, reducing the risk of complications such as stroke and heart failure.
- Improved Treatment Outcomes: Early detection enables healthcare providers to initiate appropriate treatment strategies, optimizing patient outcomes and quality of life.
- Risk Stratification: Identifying individuals at high risk of arrhythmias facilitates targeted monitoring and intervention, minimizing adverse events.
- Patient Empowerment: Accessible detection methods empower individuals to take an active role in monitoring their heart health, promoting early intervention and lifestyle modifications.
Challenges and Future Directions:
Despite significant progress, challenges remain in the field of irregular heartbeat detection:
- Accuracy: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of detection algorithms, especially in real-world settings, remains a priority.
- Integration with Healthcare Systems: Seamless integration of wearable and mobile technologies with existing healthcare infrastructure is essential for widespread adoption and clinical utility.
- Data Privacy and Security: Safeguarding sensitive health data from breaches and unauthorized access is critical to maintaining patient trust and compliance.
- Cost and Accessibility: Addressing disparities in access to advanced detection technologies is crucial for equitable healthcare delivery.
Looking ahead, future innovations in irregular heartbeat detection may focus on:

- Miniaturization: Developing smaller, more discreet monitoring devices that integrate seamlessly into everyday life.
- Personalized Medicine: Leveraging AI and big data analytics to tailor detection and treatment strategies to individual patient profiles.
- Remote Monitoring: Expanding remote monitoring capabilities to enable real-time surveillance of cardiac function, particularly in underserved or remote populations.
- Collaborative Research: Fostering interdisciplinary collaboration between clinicians, engineers, and data scientists to drive innovation and translation into clinical practice.
Conclusion:
Irregular heartbeat detection has undergone a remarkable transformation, thanks to technological advancements and innovative approaches. From wearable devices to AI-powered algorithms, these tools offer unprecedented opportunities for early detection, intervention, and personalized care. By leveraging these technologies and addressing existing challenges, we can strive towards a future where irregular heartbeat detection is accessible, accurate, and integral to cardiovascular health management.